Difference between revisions of "Tips & Tricks"
(→Using Sponge electrodes) |
(→Using Ag/AgCl Pi electrodes) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
If you have impedance issues, rewet them from a side hole using a syringe. Be careful not to wet the cap and not to spread saline solution between electrodes. | If you have impedance issues, rewet them from a side hole using a syringe. Be careful not to wet the cap and not to spread saline solution between electrodes. | ||
| − | == Using Ag/AgCl | + | == Using Ag/AgCl Pistim == |
Pi electrodes are also easy to use. You can place them on the cap and gel them (fill the electrode hole space and then some more) prior placing the cap on the subject's head. | Pi electrodes are also easy to use. You can place them on the cap and gel them (fill the electrode hole space and then some more) prior placing the cap on the subject's head. | ||
| − | If you have impedance issues, regel them from the electrode hole or a side hole using a syringe. | + | If you have impedance issues, regel them from the electrode hole or a side hole using a syringe. |
== The impedance test == | == The impedance test == | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 9 June 2017
Contents
Tips for EEG recording using Enobio or StarStim
In this page we provide some tips and tricks to work with our systems. Here are some useful resources you should also check:
- | StarStim tCS EEG recording (Jove)
- | A short introduction to NIC v1.2
- | Stimulation configuration with NIC v1.2
Plan your session well before starting
You should have a clear plan covering all the details of your recording session. Prepare to be patient, setting up an experiment always takes a bit longer than expected, and remember... the third time's the charm!
Before starting, charge your device and ensure that your battery level is above 50%.
Where do you want to place the electrodes? For how long do you want to record? Do you have a good naming scheme for your EEG files? What data formats do you want to save? Do you need accelerometry data? Do you want a line filter applied to the data (if so 50 or 60 Hz)?
Do you have an "electrode referencing scheme planned ahead? You should include in your montage construct a solution for data referencing. With our systems, data will be recorded referenced to the device electrical ground (the CMS electrode), but for data analysis, you should always reference the data to an electrode or to the electrodes average. Check this | link for more information on referencing.
Place carefully the CMS and DRL electrodes
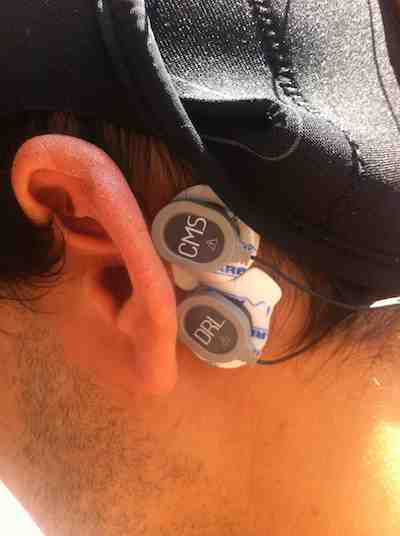
These two electrodes have to be placed over the left or right mastoid (preferably on the same side). First, clean up the mastoid area where you are going to attach the CMS/DRL electrodes. You can use a paper napkin with some water or alcohol. Removing the grease and drying the skin will help you to get a good signal.
Place the Sticktrode adhesive electrodes close to each other with the DRL on the bottom, as shown in the figure. Ensure that the two electrodes are not touching each other. The CMS electrode should be on top of the mastoid bone to avoid contamination from blood vessels (ECG like signals).
Avoid loose wires
Try to have a tidy setup with few loose wires. Loose wires are more prone to creating noise from movement.
About EEG signal quality measures in NIC
In NIC2.0 the EEG signal quality is measured for each electrode in real time.Different factors may influence the signal quality, such as the type of EEG electrodes and the CMS reference channel.
Wait few minutes for the signal to stabilize. If the quality indicator is yellow or red in all the channels, it may be related to the reference.
If the quality indicator is red only in one channel, it may be related to a bad contact between the corresponding electrode and the scalp.
Note that the quality indicator is meant to be used as a guidance, it does not need to be taken strictly. Visual inspection of the signal is equally important, which means that if the signal looks good and the indicator becomes red at some point, there is no need to immediately stop recording.
Tips for great Stimulation sessions using StarStim
See the section above for a proper placement of the DRL/CMS electrodes. They are also important for stimulation, as they are used for our impedance check (as well as EEG recording).
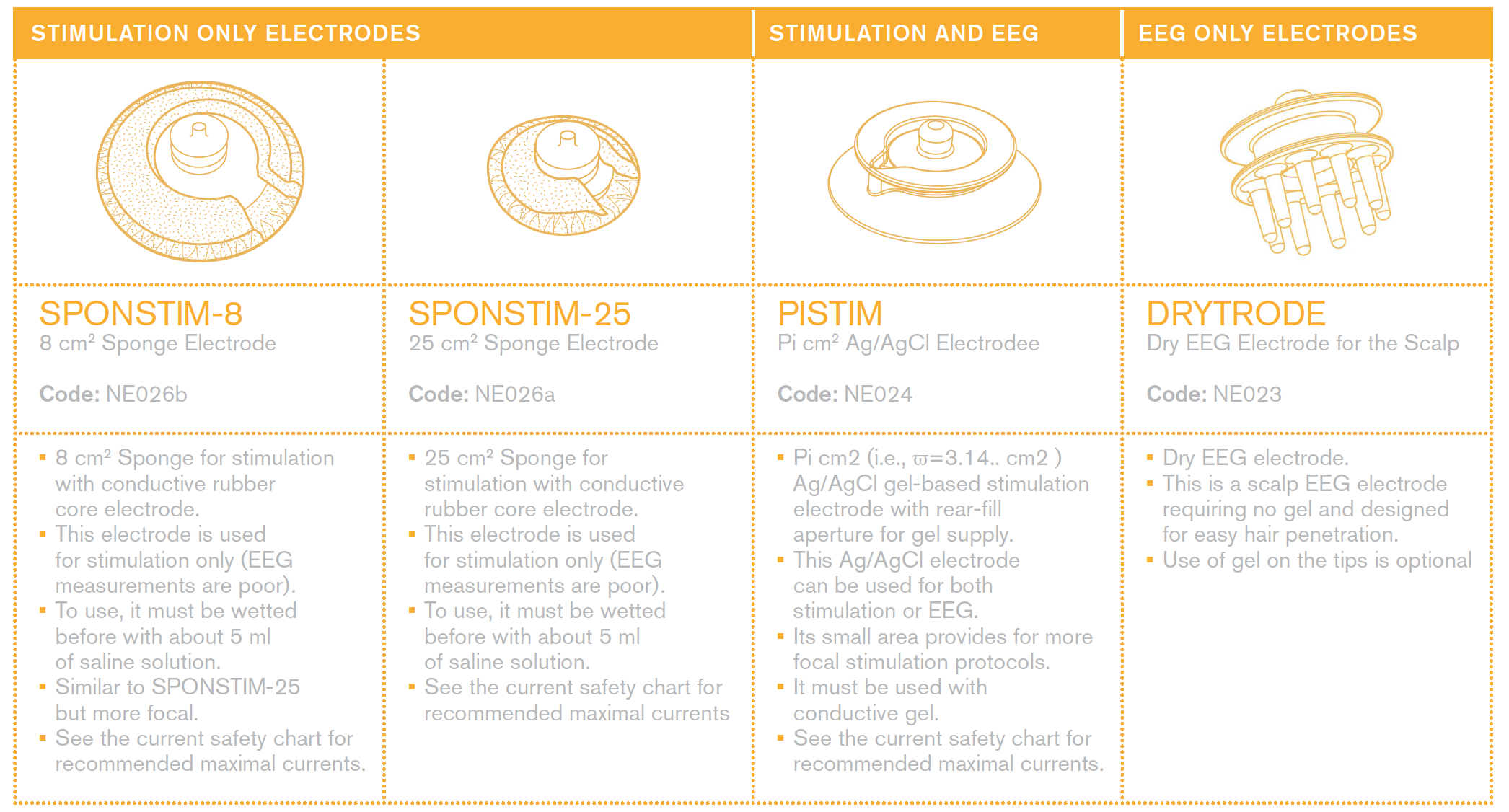
Using Sponge electrodes
Sponge electrodes are easy to use. You can place them on the cap and wet them with saline solution before placing the cap on the subject's head.
If you have impedance issues, rewet them from a side hole using a syringe. Be careful not to wet the cap and not to spread saline solution between electrodes.
Using Ag/AgCl Pistim
Pi electrodes are also easy to use. You can place them on the cap and gel them (fill the electrode hole space and then some more) prior placing the cap on the subject's head.
If you have impedance issues, regel them from the electrode hole or a side hole using a syringe.
The impedance test
You should carry out an impedance test before launching a stimulation (at least for the first session if you have several on a row with the same subject). If impedance is too high (red values) for some electrode you can follow these steps:
- Check cabling connections and recheck impedance and recheck impedance
- move the hair to ensure the contact between the electrode and the scalp
- make sure the hair is clean and free of sprays, oils, cream and lotions. Shampoo your hair and rinse with clear water the evening before or the morning of the test. Avoid hair conditioner or oil
- add more gel/saline solution (rewet or regel) to the electrodes and check again
- check that the DRL/CMS electrodes are correctly placed
- ensure that you have a reasonable battery charge (>20%)
- impedance depends on skin type and can vary quite a bit across individuals
For safety, impedance is also checked by NIC while stimulation is ongoing. If the impedance is too high, the stimulation session will self-abort.
The impedance bar appears below the icons of the stimulation channels and its color depends on the obtained value:
green: [0 - 10] kOhm
orange: [10 - 15] kOhm
red: [10 - 15] kOhm
Everything about electrodes for EEG and stimulation
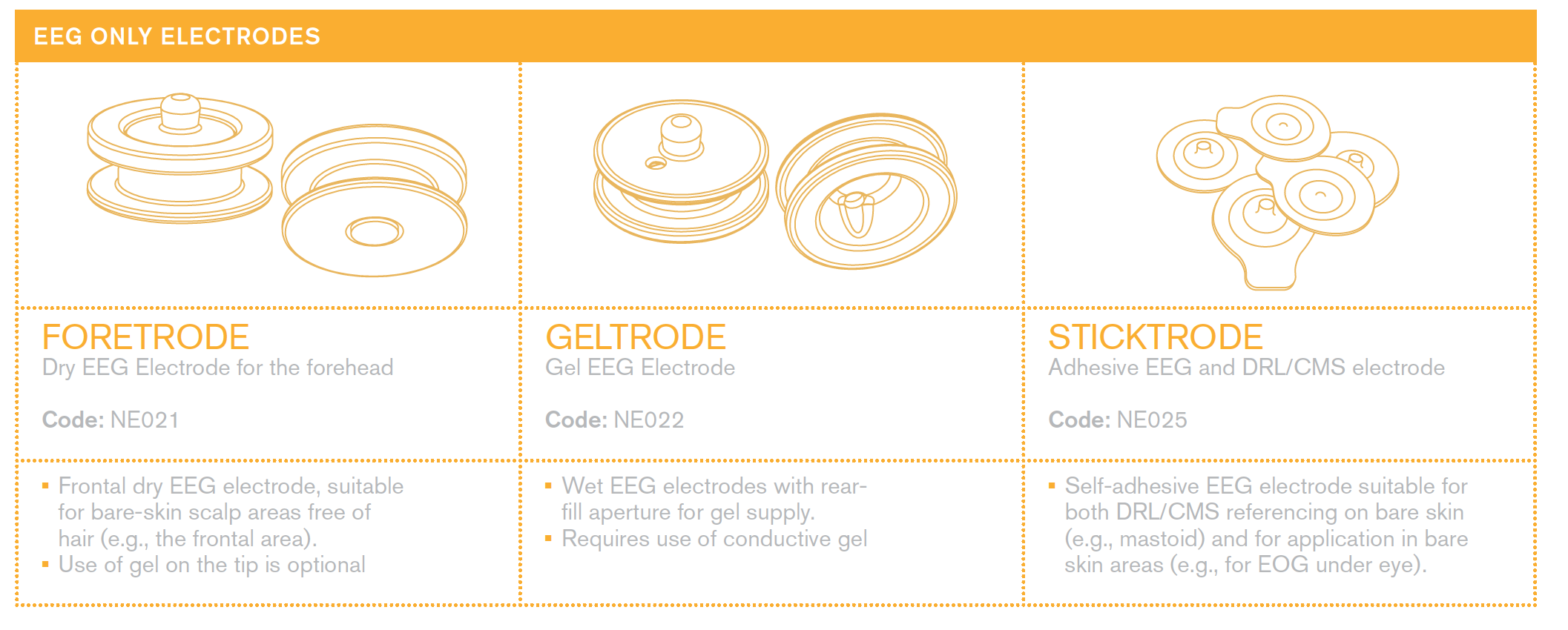
Please see the | Electrode User Manual for a description of our electrodes.
Caring for EEG electrodes
It's very important to remove all the gel from the electrodes (and cap!) carefully after a recording session using gel. You can do this with water.
Sunlight exposure or contact with metals might damage the electrodes.
With our wet electrodes some discoloration may occur after a few uses. It is normal and does not affect data quality.
Caring for stimulation electrodes
It's important to rinse stimulation electrodes (sponges and Ag/AgCl alike) with water in order to remove the salts that might remain after drying.
It is also recommended to dry the metal part to avoid salt on the connectors.
In case there salt accumulating at the metallic part, it can be washed with some vinegar to remove it.
Electrode lifetime
The number of uses or hours of recording using our EEG electrodes depends on how are they cleaned or stored. Electrode degradation can be suspected when the electrodes' signals are too noisy. If your electrodes signals are becoming noisy, replace them with new ones.
The lifetime of Ag/AgCl stimulation "Pi"-electrodes depends on their use. The electrodes degrade while passing current, but the process reverses if the direction of currents are reversed. For this reason, it is advisable to swap anode and cathode in tDCS protocols to increase electrode lifetime. Degraded electrodes will produce degraded, noisy EEG, and may give higher impedance values on Impedance Check. A rule of thumb is that a pair of electrodes used for tDCS without swapping Anode and Cathode should last for about 8 h worth of stimulation (about 24 20 minute stimulation sessions). Swapping electrodes will increase their lifetime. The lifetime for these electrodes with tACS or tRNS will be much longer.
The lifetime of sponge electrodes is very long.
Cable instructions
After each use it is important to disconnect the cables from the electrodes in order to avoid contact with both metals (metal of the electrodes and metal of the cable). If it is not disconnected the cables and also the electrodes can be damaged.
Neoprene cap cleaning and disinfecting instructions
After each use the neoprene cap or the neoprene band should be cleaned and disinfected. Use warm tap water to rinse the gel and some ivory soap to clean the cap. Dry the cap consciously using paper towel. Spray the cap with disinfectant and let sit for 10 minutes. Rinse cap thoroughly. Hang up the cap to dry.